What is an Industrial 5G Private Network?
An industrial 5G private network, also known as a 5G dedicated network, refers to a network built by enterprises using exclusive frequency spectrum for 5G deployment. It operates independently of public networks, ensuring all 5G network elements, transmission, and network management are fully controlled and operated by the enterprise. The entire 5G control plane and user plane are localized within the company, providing a tailored, private 5G network solution. Here’s an overview:
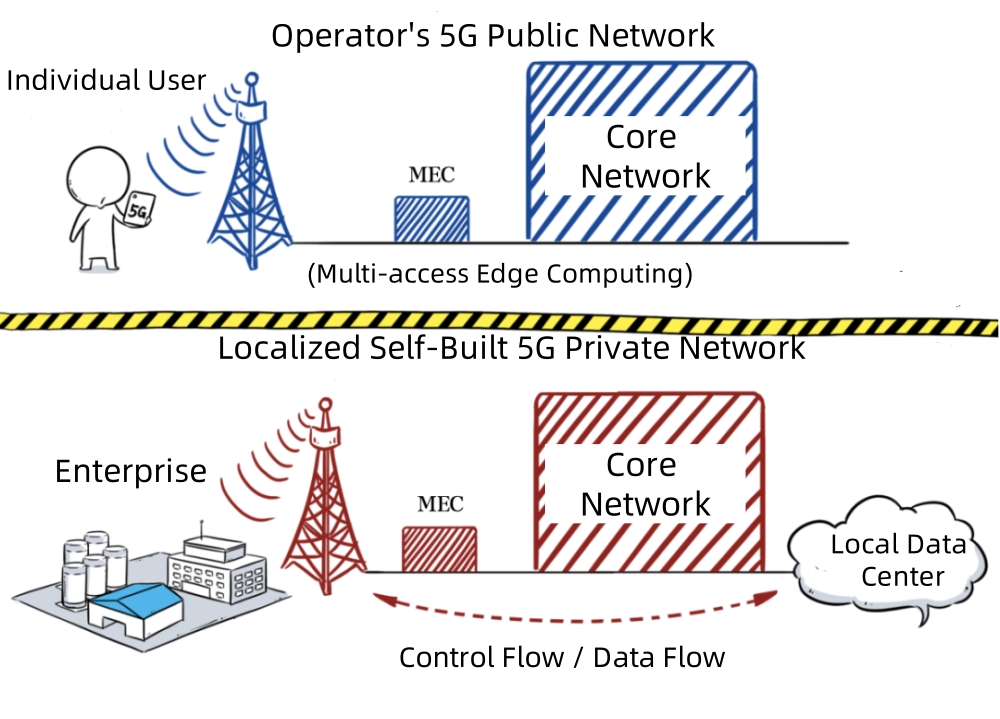
5G Public Network VS 5G Private Network
Background and Significance
With the rapid development of the Industrial Internet, there is an increasing demand for reliable, low-latency, and high uplink capacity networks for industrial applications. Traditional public 5G networks have limitations in meeting these specialized needs. Industrial 5G private networks have emerged to provide better support for large and extra-large enterprises, offering tailored network solutions to drive industrial digital transformation.
Frequency Allocation
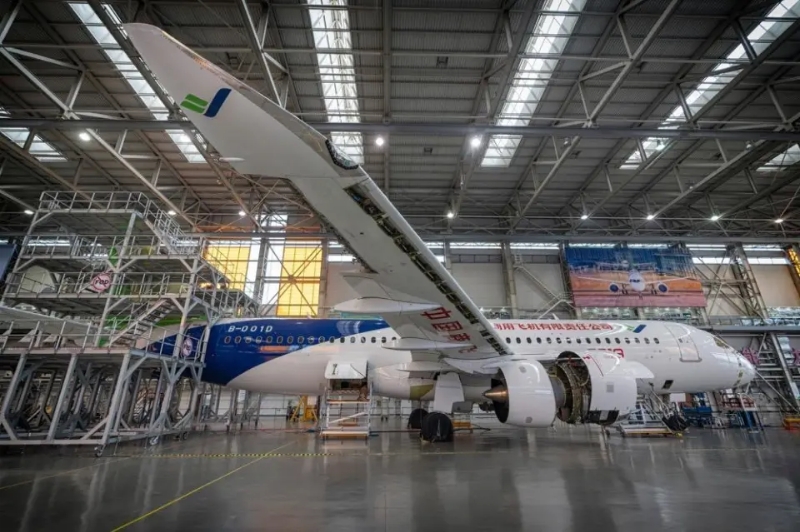
For example, in China, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has issued exclusive frequency band licenses to companies, such as the 5925-6125 MHz and 24.75-25.15 GHz bands granted to COMAC. These dedicated frequencies allow enterprises to build their independent private networks, avoiding interference from public communication services. This ensures high reliability, low latency, and other specific needs while also reducing Customer Premises Equipment (CPE) costs.
Airplane Industrial
Comparison with Other 5G Private Network Models
Public Network Integration Mode: This includes hybrid private networks, which share part of the public network, and virtual private networks, which share end-to-end network infrastructure with the public network. Many of the 5G private networks offered by China’s major carriers are based on the public network integration model. These networks extend private network services over a public infrastructure, providing enterprises with customized solutions. However, the industrial 5G private network is entirely independent from the public network, with significant differences in frequency allocation, network architecture, and management, offering higher security and autonomy.
Non-Independent Deployment Mode: In this mode, 5G private networks rely on existing 4G networks, using the 4G core network and 5G radio access network. While this allows for quick 5G service deployment, it offers limited 5G functionality. Industrial 5G private networks, on the other hand, adopt an independent deployment model, delivering full 5G capabilities to meet the strict network performance requirements of industrial production.
Advantages
1.Differentiated Local Services: Enterprises can tailor the network coverage and services based on regional and business needs, better adapting to the diverse requirements of various industrial scenarios.
2.Customizable Network Build Costs: Companies can build a network architecture that suits their scale and budget, minimizing resource waste or shortages and maximizing cost efficiency.
3.Flexible Security Control: Enterprises can set stringent security policies to protect core data and production processes, ensuring high standards of data security and privacy protection in industrial environments.
4.Supports Personalized Self-Service: Enterprises can independently manage and optimize network resource allocation, adjusting configurations based on evolving business needs to enhance network efficiency and flexibility.
Application of 5G Mobile Signal Boosters in Industrial Manufacturing
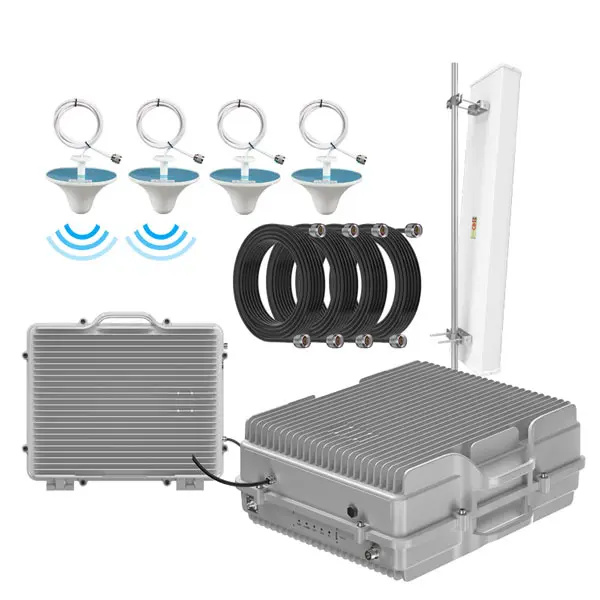
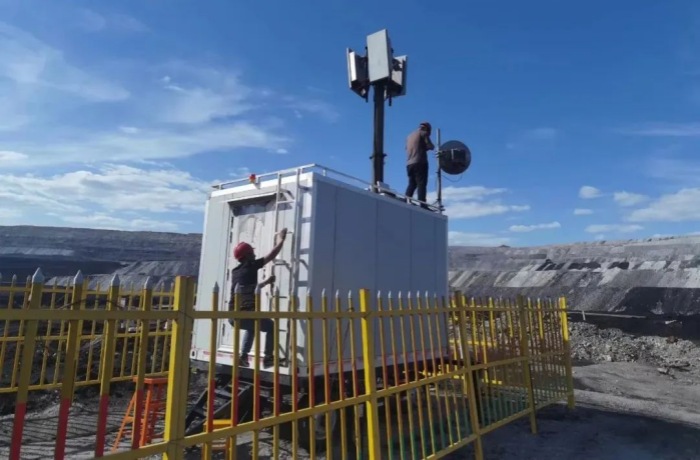
In industrial environments, 5G mobile signal boosters or fiber optic repeaters are essential for ensuring strong and reliable 5G signal coverage within buildings. Companies can work with mobile signal booster manufacturers to customize solutions tailored to their specific 5G frequency bands. From repeaters to antennas, all components can be tailored for optimal performance. Lintratek, with 13 years of experience in manufacturing mobile signal boosters, fiber optic repeaters, and antennas, is well-equipped to provide custom 5G solutions for enterprises driving the digital revolution.
Some Key Applications of Industrial 5G Signal Boosters:
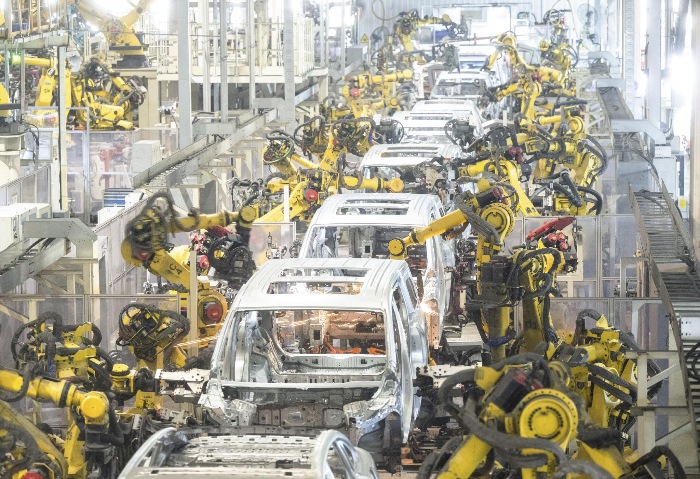
Device Connectivity and Data Collection: In large factories with numerous production devices such as CNC machines, robots, and automated production lines, 5G signal boosters can enhance signal coverage, ensuring stable and high-speed data transmission between devices. This enables real-time monitoring and data collection of production processes. For example, robots can transmit their operational status, fault data, and more via 5G networks, allowing technicians to make timely adjustments and improve production efficiency. Additionally, industrial sensors can transmit data such as temperature, pressure, and humidity to central data systems for environmental and equipment monitoring.
Remote Control and Operations: In industries such as chemicals and mining, where operations may occur in hazardous environments or require precise control, remote control becomes vital. 5G mobile signal boosters ensure stable signal transmission for remote control, allowing operators to safely control robots, automated forklifts, and other equipment from a distance, reducing personnel risk. Experts can also provide real-time remote guidance to on-site workers, improving operational accuracy and efficiency.
Smart Quality Inspection: Utilizing 5G’s high-speed transmission and low latency, combined with high-definition cameras and sensors, 5G signal boosters enable real-time product quality inspection on production lines. In the automotive industry, for example, high-resolution camera images of car parts can be transmitted quickly via 5G to quality control systems. AI algorithms analyze these images to detect defects and alert workers, improving product quality and production efficiency.
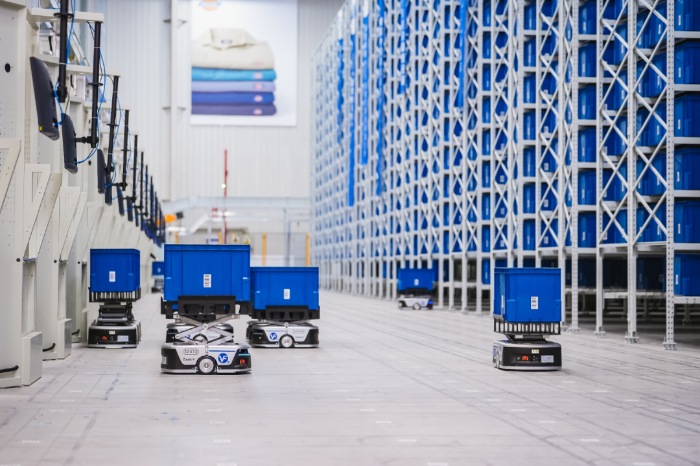
Smart Warehousing and Logistics: In smart warehouse management, 5G mobile signal boosters ensure stable communication between AGVs (Automated Guided Vehicles), AMRs (Autonomous Mobile Robots), and the warehouse management system. These devices receive real-time instructions and perform tasks such as material handling, storage, and retrieval efficiently. In logistics, 5G signal boosters help track vehicles and goods, enabling real-time location updates and facilitating intelligent scheduling.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) for Production Assistance: VR and AR technologies are increasingly applied in design, training, and maintenance within industrial manufacturing. 5G signal boosters provide stable network connectivity for VR/AR devices, enabling virtual design reviews and training simulations. With 5G, operators can receive real-time instructions and virtual annotations, improving operational efficiency and reducing training time and costs.
Cloud-Based Manufacturing and Edge Computing: 5G mobile signal boosters play a key role in enabling the transition to cloud-based manufacturing, allowing production equipment to connect seamlessly to the cloud for resource sharing and optimization. Combined with edge computing, these boosters ensure fast data transmission between edge nodes and the cloud, reducing latency and enhancing system responsiveness for real-time production optimization and smart decision-making.
Post time: Dec-20-2024